You hear about artificial intelligence everywhere, but you don't really know what it is? You're not alone. Between ChatGPT, self-driving cars, and Netflix recommendations, AI has become omnipresent without us always understanding how it works.
In this comprehensive guide, I'll explain simply what AI is, how it works, what the different types of artificial intelligence are, and most importantly what artificial intelligence is used for in your daily life. As a bonus, I'll reveal who invented this fascinating field.
In this article
What is artificial intelligence?
Artificial intelligence (AI) refers to a set of computer techniques that enable systems to perform tasks that typically require human intelligence: perception, learning, reasoning, decision-making, language understanding.
In simpler terms, AI is when a machine can "understand," "learn," and "decide" as a human would. When you ask Siri to set an alarm or Google Translate translates a sentence, AI is at work.
Simple definition: AI is a scientific and technical field aimed at building systems capable of accomplishing tasks that normally require human intelligence (reasoning, learning, perceiving, understanding language).
Contrary to what you might think, AI is not a single technology, but a set of methods (algorithms, models, architectures) capable of analyzing large volumes of data, detecting patterns, and making decisions or recommendations.
What is AI used for?
Artificial intelligence is present everywhere in our daily lives, often without us realizing it. Here are the main applications:
In industry and services
- Predictive maintenance: AI detects failures before they occur
- Logistics optimization: delivery planning and inventory management
- Fraud detection: real-time analysis of banking transactions
- Product recommendations: personalized suggestions on Amazon, Netflix, Spotify
- Process automation: chatbots, automatic email sorting
In everyday life
- Voice assistants: Siri, Alexa, Google Assistant
- Automatic translation: Google Translate, DeepL
- Image recognition: facial unlock, Google Photos
- Assisted vehicles: Tesla Autopilot, parking assistance
- Creative tools: ChatGPT, Claude, Midjourney for generating text and images
In healthcare
- Medical diagnosis: cancer detection on medical imaging
- Drug discovery: accelerating pharmaceutical research
- Patient monitoring: connected health applications
How does artificial intelligence work?
AI systems rely on algorithms that manipulate data to recognize patterns, learn input-output relationships, and optimize an objective function (error, reward, probability).
Concretely, here's how it works in 3 steps:
1. Data collection
AI needs data to learn. The more quality data it has, the better it will perform. For example, to create a spam detector, you show it thousands of spam and non-spam emails.
2. Model training
The algorithm analyzes the data and adjusts its internal parameters to minimize errors. It's like teaching a child: you show them examples until they understand the pattern.
3. Prediction and decision
Once trained, the model can analyze new data it has never seen and make predictions or decisions.
Important: Current AI is not "intelligent" in the human sense. It doesn't really understand what it's doing. It detects statistical patterns in data, which can lead to errors or "hallucinations."
The different types of AI
There are several categories of artificial intelligence, organized hierarchically:
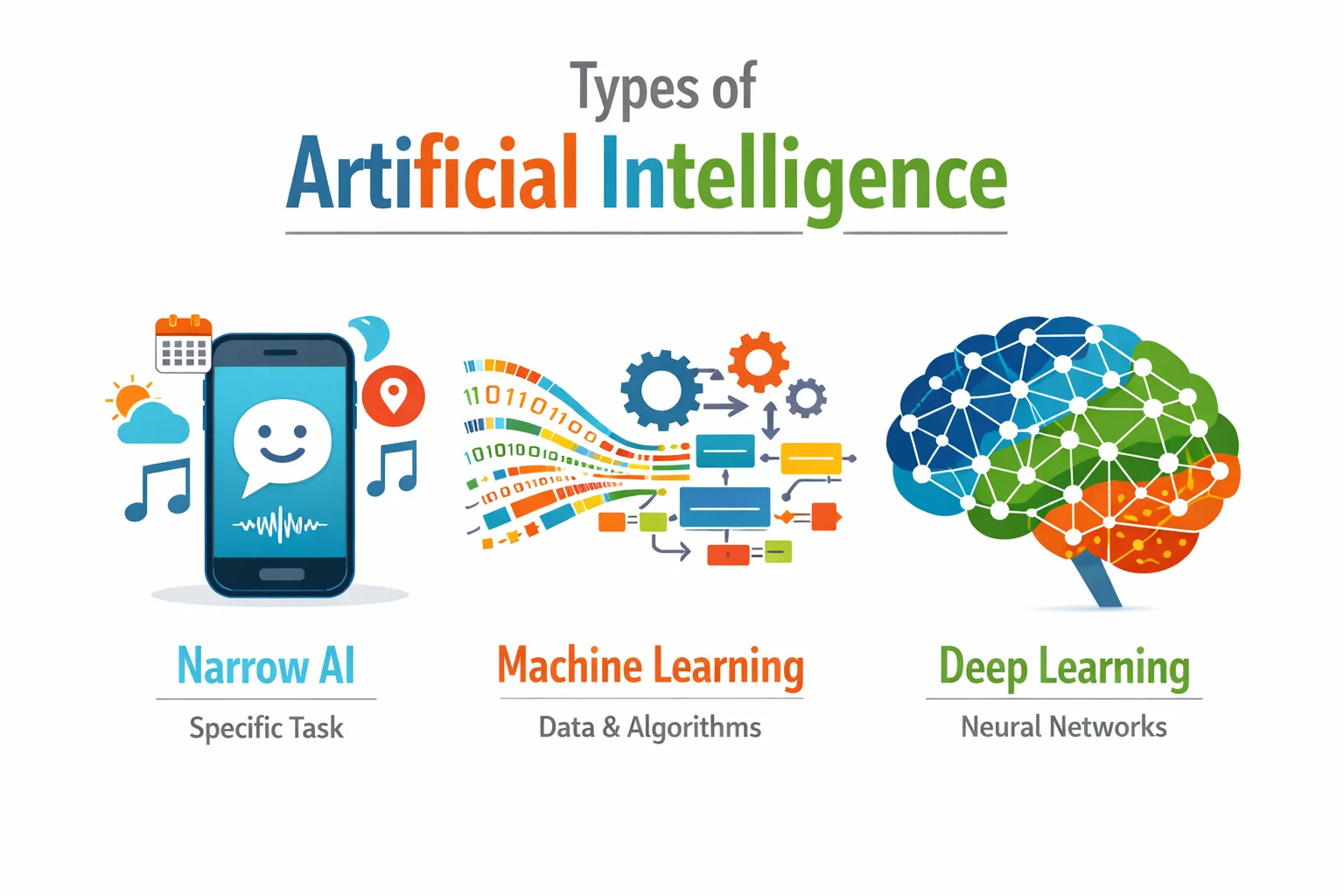
Machine Learning
Machine Learning refers to methods where a model learns from data rather than being fully programmed by hand. There are three main types:
- Supervised learning: labeled examples are provided (e.g., "this email is spam")
- Unsupervised learning: the algorithm finds patterns without labels
- Reinforcement learning: the agent learns through trial and error with rewards
Deep Learning
Deep Learning is a subset of Machine Learning that uses deep neural networks (multiple layers) to learn hierarchical representations from complex data (images, text, audio, time series).
It's the technology behind facial recognition, modern automatic translation, and voice assistants.
Generative AI
Generative AI encompasses models capable of producing new content (text, image, audio, code, video) from learned distributions. Large language models (GPT-4, Claude) and image generators (Midjourney, DALL-E) rely on deep learning techniques.
| Type of AI | Definition | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Machine Learning | Algorithms that learn from data | Spam detection, recommendations |
| Deep Learning | Multi-layer neural networks | Facial recognition, translation |
| Generative AI | Models that create new content | ChatGPT, Midjourney, Sora |
Who invented artificial intelligence?
The term "artificial intelligence" was formalized in the mid-1950s by John McCarthy, particularly in the context of the Dartmouth Conference in 1956, considered the official birth of the field.
However, Alan Turing is a foundational figure who, without using the term AI, provided the conceptual framework and test (imitation game or Turing test) that strongly influenced the modern field. As early as 1950, Turing asked the question: "Can machines think?"
Major milestones in AI history
- 1950: Alan Turing proposes the "Turing Test"
- 1956: Dartmouth Conference - official birth of AI
- 1960-1970: First expert systems
- 1980-1990: "AI Winter" - period of disillusionment
- 1997: Deep Blue (IBM) beats Kasparov at chess
- 2012: Deep Learning revolution with AlexNet
- 2016: AlphaGo (Google) beats the world champion of Go
- 2022: ChatGPT launches the generative AI revolution
- 2024-2026: Explosion of AI agents and multimodal models
Generative AI vs Traditional AI
The main difference between traditional AI and generative AI lies in their objective:
| Criteria | Traditional AI | Generative AI |
|---|---|---|
| Objective | Analyze, classify, predict | Create new content |
| Output | Category, score, decision | Text, image, audio, video, code |
| Examples | Spam filter, credit scoring | ChatGPT, Midjourney, Sora |
| Interaction | Automatic in the background | Conversational via prompts |
Generative AI has revolutionized our relationship with artificial intelligence by making it accessible to everyone through simple interfaces like ChatGPT or Claude.
Risks and challenges of AI
Authorities and standardization bodies highlight major challenges:
! Main risks
- - Algorithmic bias: unintentional discrimination
- - Data protection: threatened privacy
- - Transparency: "black box" effect
- - Liability: who is responsible for errors?
- - Misinformation: deepfakes and false information
? Societal concerns
- - Impact on employment and jobs
- - Concentration of technological power
- - Use in surveillance
- - Military applications
- - Inequalities in technology access
These concerns have motivated the creation of regulatory frameworks (such as the European AI Act), ethical charters, and AI-specific standards. The challenge is to develop responsible and ethical AI.
FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions About Artificial Intelligence
What is artificial intelligence in simple terms?
Artificial intelligence (AI) refers to a set of technologies that enable machines to perform tasks that typically require human intelligence: understanding language, recognizing images, making decisions, or learning new things. Concretely, when you use ChatGPT to write an email or Netflix recommends a movie, AI is working behind the scenes.
Who invented artificial intelligence?
The term "artificial intelligence" was coined by John McCarthy in 1956 at the Dartmouth Conference, considered the official birth of the field. However, the conceptual foundations were laid by Alan Turing as early as 1950 with his famous imitation test (Turing test) to determine whether a machine can think.
What is the difference between AI, Machine Learning and Deep Learning?
AI is the overarching field that encompasses all techniques enabling machines to mimic human intelligence. Machine Learning is a branch of AI where algorithms learn from data. Deep Learning is a subset of Machine Learning that uses deep neural networks, particularly effective for processing complex data like images or text.
What is artificial intelligence used for in everyday life?
AI is everywhere in our daily lives: voice assistants (Siri, Alexa), automatic translation (Google Translate), personalized recommendations (Netflix, Spotify), spam filters, GPS with traffic prediction, facial recognition on our smartphones, and of course chatbots like ChatGPT or Claude for writing and assistance.
Is artificial intelligence dangerous?
AI presents risks that must be taken seriously: algorithmic biases that can lead to discrimination, data privacy issues, impact on employment in certain sectors, and risks of misinformation. However, these risks are managed through regulations (like the European AI Act) and best practices. The challenge is to use AI responsibly and ethically.
What is generative AI?
Generative AI is a category of artificial intelligence capable of creating new content: text (ChatGPT, Claude), images (Midjourney, DALL-E), audio, video, or code. These models learn from enormous amounts of data to then generate original content. It's the technology behind the current AI revolution for the general public.
Conclusion
Artificial intelligence is a major technological revolution transforming our daily lives and the way we work. From simple Netflix recommendations to autonomous vehicles, through ChatGPT and creative tools, AI is everywhere.
Remember the essentials: AI is not a single technology but a set of methods (Machine Learning, Deep Learning, Generative AI) that enable machines to learn and perform intelligent tasks. Officially invented in 1956, it is experiencing unprecedented acceleration today with generative AI.
What matters now? Learning to use these tools to save time and be more efficient, while remaining aware of ethical issues. And good news, I've written a comprehensive guide on how to use AI!
Stay informed about AI
Get my best AI tools and tips delivered to your inbox every week.

